Welcome to the world of gardening, where the earthy scent of soil and the vibrant colors of plants greet you with every step. Amidst this vibrant tapestry, one of the essential elements you’ll encounter in gardening is peat moss.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover everything about peat moss, from what it is, how it’s used, its pros and cons, environmental concerns, alternatives, and much more. By the end of this article, you’ll have a solid understanding of peat moss and how it can enhance your gardening experience.
Jump to a section:
What is Peat Moss?
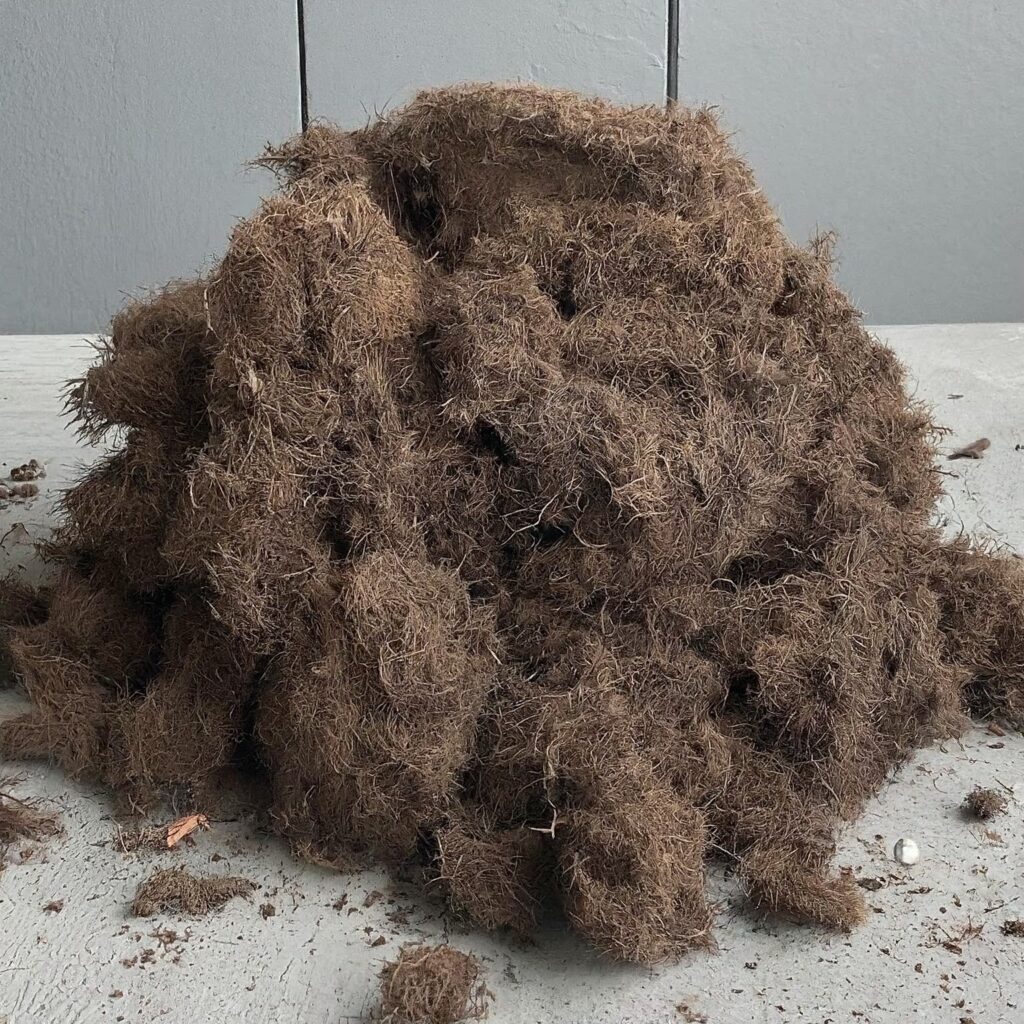

Peat moss, often referred to simply as “peat,” is a natural organic material derived from decomposed sphagnum moss and other organic matter found in peat bogs.
These bogs are waterlogged areas where plant material accumulates over thousands of years, undergoing partial decomposition due to the acidic and anaerobic conditions.
The result is a dense, fibrous material with excellent water retention properties. That’s called peat moss.
Peat Moss Uses
So, what is what is peat moss used for, you ask?
Well, peat moss soil has numerous applications in gardening and horticulture.
One of its primary uses is as a soil amendment to improve soil structure and water retention. When mixed with soil, peat moss helps loosen compacted soil, allowing for better root penetration and drainage.
It also acts as a sponge, absorbing excess moisture and releasing it gradually to plant roots, thus promoting healthy growth.
What’s more, peat moss is commonly used in potting mixes and seed-starting blends due to its lightweight nature and ability to hold moisture. Its sterile properties make it an excellent medium for starting seeds and rooting cuttings, providing an optimal environment for germination and root development.
What Plants Like Peat Moss?
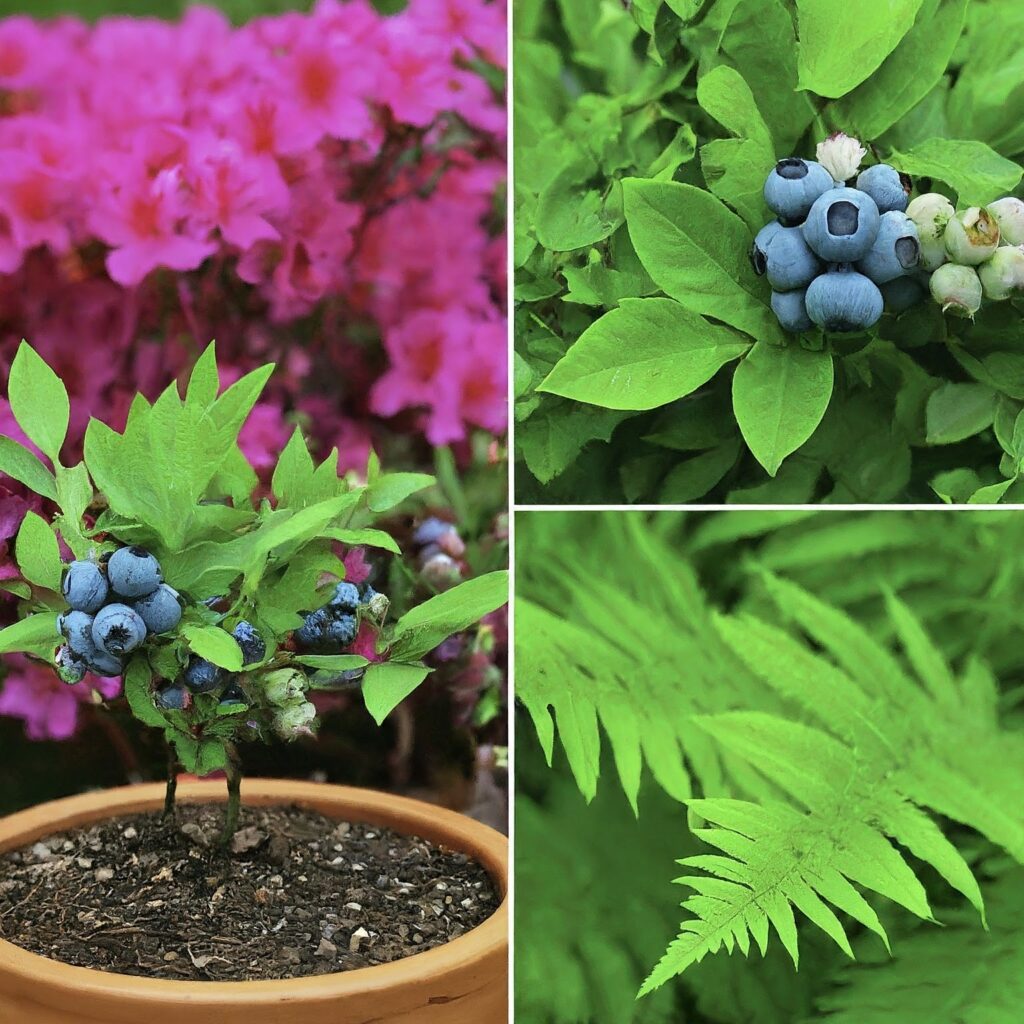

Peat moss is favored by a wide range of plants, particularly those that thrive in acidic soil conditions.
Acid-loving plants such as azaleas, rhododendrons, blueberries, and camellias benefit greatly from the presence of peat moss in the soil.
Its ability to lower the pH level of soil makes it an ideal growing medium for these plants, providing them with the acidic environment they need to thrive.
How to Make Peat Moss
While peat moss forms naturally over thousands of years in peat bogs, you can create a similar material on a smaller scale for your gardening needs.
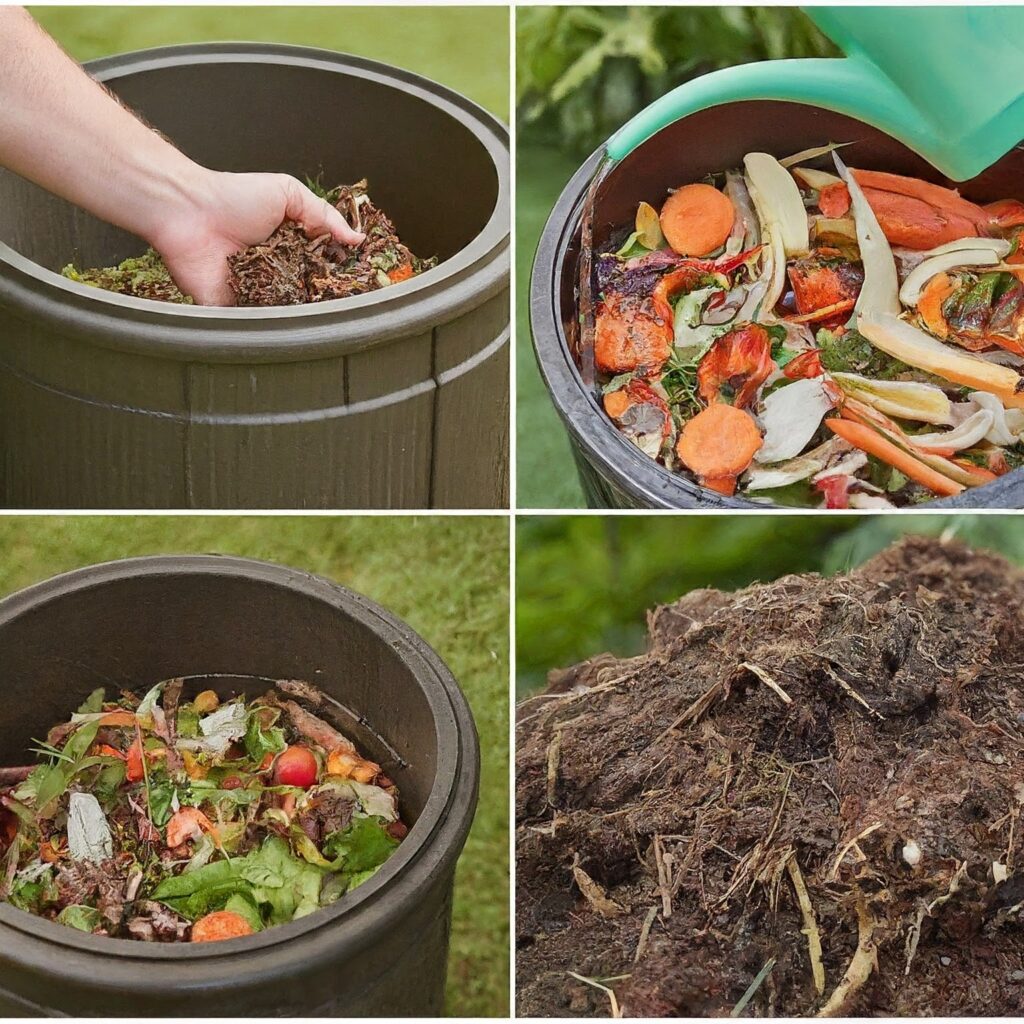

To make peat moss at home, you’ll need to gather organic materials, such as sphagnum moss, leaves, and other plant debris. Next, layer these materials in a container or compost bin, keeping them moist and aerated.
Over time, microbial activity will break down the organic matter, eventually forming peat-like material you can use in your garden.
Peat Moss Pros and Cons
Like any gardening material, peat moss has its pros and cons. Let’s explore some of them:
Pros:
- Excellent water retention properties
- Improves soil structure and aeration
- Acidifies soil for acid-loving plants
- Lightweight and easy to work with
- Sterile and free from weed seeds
Cons:
- Non-renewable resource
- Harvesting can damage peat bog ecosystems
- May become compacted over time
- pH can become too acidic if overused
The good news is that peat moss alternatives are available for sustainable gardening practices.
Environmental Concerns of Peat Moss Harvesting
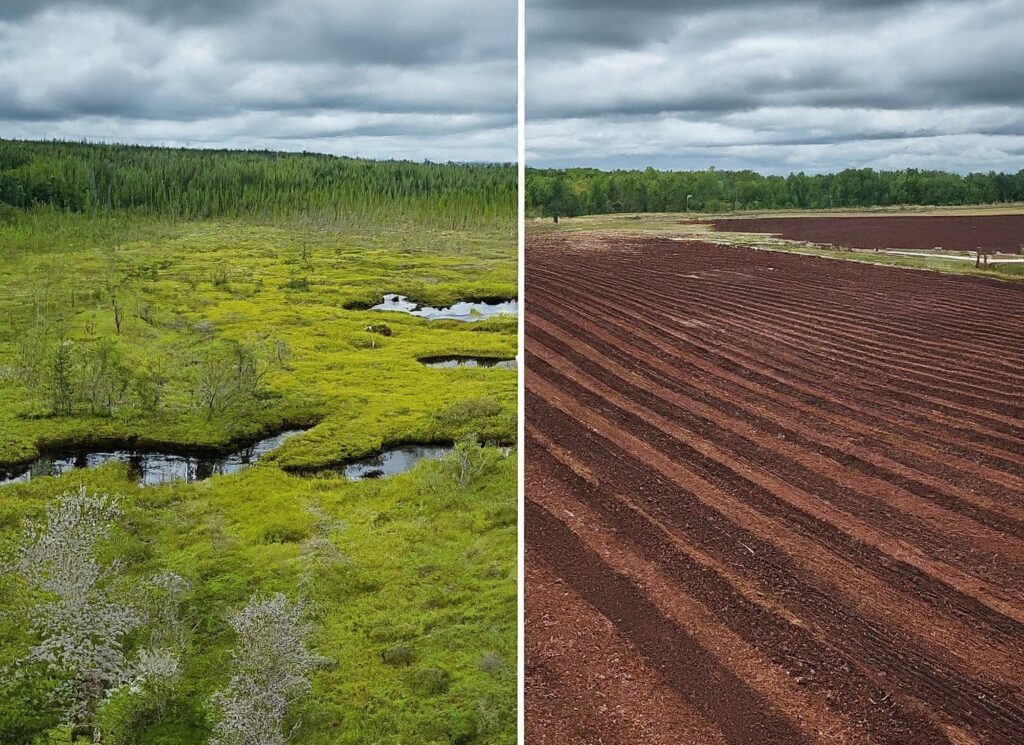

While peat moss offers valuable benefits to gardeners, its extraction raises significant environmental concerns.
Peat bogs are delicate ecosystems that support unique plant and animal species, including rare and endangered ones. Harvesting peat moss disrupts these ecosystems, leading to habitat loss, carbon emissions, and loss of biodiversity.
Furthermore, peat bogs act as carbon sinks, storing large amounts of carbon dioxide. These bogs release stored carbon into the atmosphere when disturbed through drainage or excavation, contributing to climate change.
Therefore, you may want to look for a peat moss alternative for more sustainable gardening.
Peat Moss Alternative
Fortunately, several alternatives to peat moss are available for eco-conscious gardeners.

Coconut coir, also known as coco coir, is one such alternative. Made from the fibrous husk of coconut shells, coconut coir is renewable, sustainable, and environmentally friendly. It offers similar water retention properties to peat moss and can be used as a soil amendment, potting mix ingredient, or seed starting medium.
Other alternatives include compost, leaf mold, and well-aged manure, all of which can improve soil structure and fertility without the environmental impact associated with peat moss extraction.
Peat Moss vs Sphagnum Moss
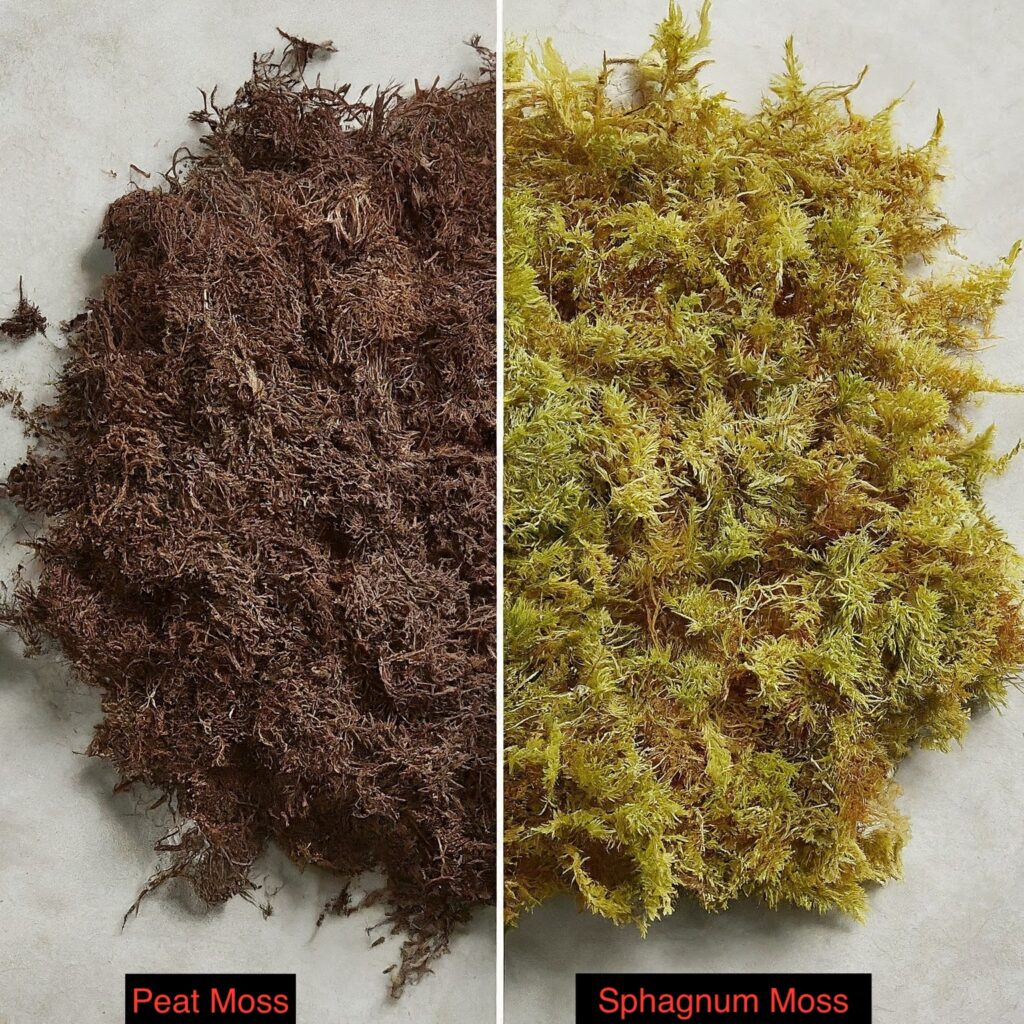

Sphagnum moss and peat moss are often mixed up, but they’re actually different parts of the same plant and have very different effects on the environment.
It’s worth noting that sphagnum moss grows on soil or in swamps, especially in wet places like New Zealand. It’s harvested carefully to make sure the swamps can keep growing, which usually takes about 5-6 years. Sphagnum moss is alive and helps the environment by soaking up water and nutrients, providing homes for animals, and trapping carbon.
On the other hand, peat moss, also known as peat, is what happens when sphagnum moss decomposes over thousands of years. It forms thick layers under the surface of bogs. While it holds water like sphagnum moss, harvesting peat moss is a big problem for the environment.
Digging up bogs to get it ruins the homes of many plants and animals. Plus, peat moss takes forever to come back, so it’s not a renewable resource.
Sphagnum moss is harvested in its living state and used mainly in horticulture for lining hanging baskets, creating decorative arrangements, and providing moisture retention in plant containers.
How to Use Peat Moss
Using peat moss in your garden is relatively straightforward. Here are some tips for incorporating it into your gardening practices:
- Soil Amendment: Mix peat moss and soil to improve its structure, aeration, and water retention. Aim for a ratio of one part peat moss to three parts soil for best results.
- Potting Mix: Include peat moss in your homemade potting mix or purchase pre-made mixes that contain peat moss. This will provide your potted plants with the moisture they need to thrive.
- Seed Starting: Create a seed starting mix by combining peat moss with perlite or vermiculite. This lightweight, sterile medium will support seed germination and early seedling growth.
- Mulching: Apply a layer of peat moss around your plants as a mulch to help retain soil moisture and suppress weeds. Ensure the soil is moist before applying the mulch to prevent it from drying out.
Peat Moss FAQs
1. How long does peat moss last?
Peat moss can last for several years when stored properly in a cool, dry place. However, its effectiveness may diminish over time, especially if it becomes compacted or saturated with minerals.
2. Does peat moss need soil?
While peat moss can be used alone in some gardening applications, it is often mixed with soil to improve its structure and water retention. Using peat moss alone may lead to issues such as compaction and nutrient deficiencies.
3. How does peat moss affect plant growth?
Peat moss enhances plant growth by improving soil structure, increasing water retention, and acidifying the soil for acid-loving plants. It provides an optimal environment for root development and nutrient uptake.
4. Does peat moss absorb moisture?
Yes, peat moss is highly absorbent and can hold up to 20 times its weight in water. This makes it an excellent medium for retaining moisture in the soil and providing a consistent water supply to plant roots.
5. Is sphagnum moss more sustainable than peat moss?
Sphagnum moss, when harvested sustainably, can be more environmentally friendly than peat moss. However, both materials have associated environmental concerns, and gardeners may opt for alternative growing mediums to minimize their ecological footprint.
6. Where does peat moss come from?
Peat moss is primarily harvested from peat bogs, which are wetland ecosystems characterized by soggy conditions and the accumulation of organic matter. These bogs are found in various regions worldwide, including North America, Europe, and Asia.
7. Is peat moss acidic?
Yes, peat moss is acidic. It naturally has a low pH level, which means it tends to make soil more acidic when mixed with it. This acidity is beneficial for plants that thrive in acidic conditions, such as azaleas, rhododendrons, blueberries, and camellias.
Conclusion
As you can see, peat moss is a valuable resource for gardeners, offering numerous benefits for soil improvement, plant growth, and moisture retention. However, its extraction raises significant environmental concerns, prompting many gardeners to seek sustainable alternatives.
Make sure to understand the properties of peat moss, its uses, and its environmental impact so you can make informed choices for your gardening practices.
Whether you choose to incorporate peat moss into your garden or explore alternative options, may your gardening journey be filled with joy, growth, and abundance.