As someone new to gardening, one of the first things you’ll encounter is potting mix. Whether you’re planning to grow vibrant flowers, indoor plants, lush vegetables, or a collection of unique succulents, the right potting mix can make all the difference.
But what is potting mix, and why is it so crucial? Are there certain types of potting mix available? How can you create your own potting mix at home?
Read on for answers to the above questions and much more.
Jump to a section:
What is Potting Mix?

You might be wondering, what is potting mix?
Simply put, a potting mix is a blend of various ingredients meant to create an optimal growing environment for potted plants.
Unlike garden soil, which can be too dense and may not drain well, potting mix is light, airy, and specifically formulated to support the needs of plants grown in containers.
Potting mix is different from traditional soil in several key ways.
- It’s free of contaminants like weeds, pests, and diseases, which can harm your plants.
- Potting mix is lightweight, making it easier for roots to grow and access the air and water they need.
- The ingredients used in a potting mix provide the right balance of nutrients, water retention, and drainage, ensuring that your plants have everything they need to thrive.
Why Use Potting Mix in Gardening?

Using potting mix in gardening offers several benefits:
Excellent Drainage
One of the primary advantages of potting mix is its superior drainage.
Garden soil can often become compacted and waterlogged, which can lead to root rot and other issues.
Potting mix, on the other hand, is light and porous, allowing excess water to drain away quickly. This is particularly important for container gardening, where water doesn’t have anywhere to go but down.
Nutrient Availability
Potting mixes are often rich in essential nutrients that support plant growth. These nutrients are readily available to the plant roots, ensuring that your plants get off to a good start.
Many potting mixes also include slow-release fertilizers, which provide a steady supply of nutrients over time.
Aeration
A good mix ensures that air can reach the plant roots, promoting healthy root development.
Without adequate aeration, roots can suffocate, leading to poor plant growth and even death. The airy structure of the potting mix helps prevent this by keeping the soil loose and allowing air to circulate freely.
Sterility
Commercial potting mixes are typically sterilized to kill off any pests, diseases, or weed seeds. This means you’re starting with a clean slate, which is particularly important for delicate seedlings or plants that are prone to disease.
Lightweight
Potting mix is much lighter than garden soil, making it easier to handle and transport.
This is especially helpful if you’re working with large containers or if you have physical limitations that make lifting heavy bags of soil difficult.
Potting Mix Types
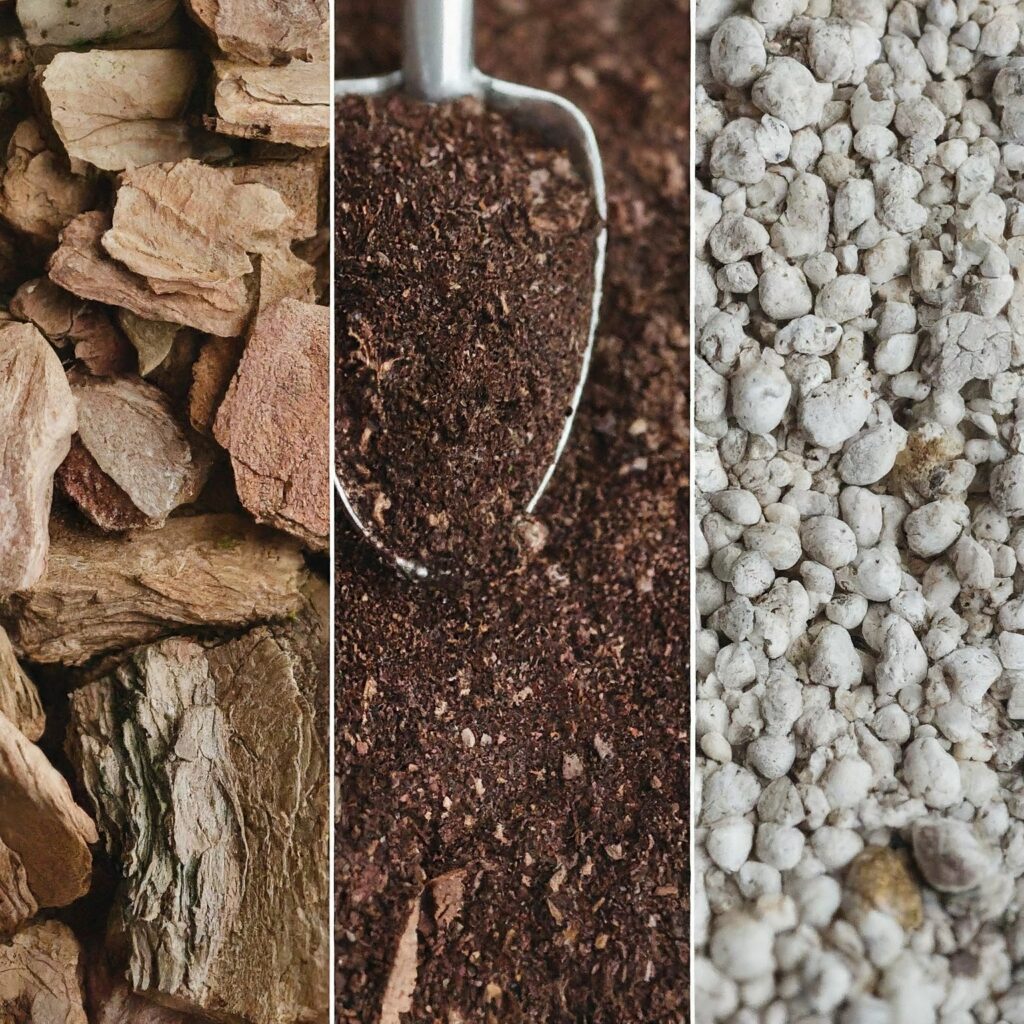

There are various types of potting mix, each tailored to different kinds of plants and gardening needs.
Let’s look at some of the most common mix types:
General Potting Mix
This is an all-purpose potting mix that works well for most houseplants, flowers, and vegetables. It typically contains a blend of peat moss, pine bark, and perlite or vermiculite.
General potting mix is a versatile option that provides a good balance of drainage, aeration, and nutrient retention, making it suitable for a wide range of plants.
Soilless Potting Mix
A soilless potting mix doesn’t contain any soil at all. Instead, it’s made up of materials like peat moss, coconut coir, perlite, and vermiculite.
This type of mix is excellent for seed-starting and sensitive plants that need a sterile environment.
Soilless mixes are often used in hydroponics and other soilless growing systems because they provide a consistent, clean growing medium.
Succulent Potting Mix
If you want to grow cacti and succulents, you’ll need a succulent potting mix.
This mix has superior drainage properties, often containing sand or fine gravel to mimic the natural environment of these drought-tolerant plants.
Succulents are particularly susceptible to root rot, so it’s crucial that their potting mix allows water to drain away quickly and doesn’t retain too much moisture.
Organic Potting Mix
An organic potting mix is made from natural and sustainable ingredients. It’s a great choice if you’re growing edible plants or if you prefer an eco-friendly approach to gardening.
Organic mixes often include compost, earthworm castings, and other organic matter that provide a rich source of nutrients and help support a healthy soil ecosystem.
Seed Starting Mix
Seed starting mix is a very fine, lightweight mix made specifically for germinating seeds. It usually contains a blend of peat moss or coconut coir and vermiculite or perlite.
This mix provides the right balance of moisture retention and aeration, creating an ideal environment for seedlings to sprout and grow strong roots.
Cactus and Palm Mix
Similar to succulent potting mix, cactus and palm mix is best for plants that require excellent drainage. It often includes sand, perlite, and small stones or gravel.
This mix helps prevent water from sitting around the roots, which can cause rot in these types of plants.
Orchid Mix
Orchids have unique requirements, and a regular potting mix won’t do. Orchid mix typically contains large pieces of bark, charcoal, and sometimes perlite or sphagnum moss.
This chunky mix allows air to circulate around the roots and provides the right support and moisture retention that orchids need.
African Violet Mix
African violets need a special potting mix that retains moisture but also provides good aeration. This mix usually includes peat moss, vermiculite, and perlite.
The balance ensures that the delicate roots of African violets are supported without becoming waterlogged.
Bonsai Mix
Bonsai trees require a well-draining mix that supports their delicate root systems while allowing excess water to drain away quickly.
Bonsai mix often contains a blend of akadama (a type of clay granule), pumice, and lava rock.
This mix helps maintain the right balance of moisture and air around the roots, which is essential for the health and development of bonsai trees.
Acid-Loving Plant Mix
Plants like azaleas, camellias, and rhododendrons thrive in acidic soil.
An acid-loving plant mix is specifically formulated to provide the low pH environment these plants need. This mix typically includes peat moss, which naturally has a lower pH, and other ingredients that help maintain the desired acidity.
Raised Bed Mix
It’s no secret that raised beds offer many benefits in gardening. While it requires a different approach than container gardening, a specialized potting mix can still be beneficial.
Raised bed mix is usually a blend of garden soil, compost, and additional materials like perlite or vermiculite to improve drainage and aeration.
This mix helps create an optimal growing environment in the confined space of a raised bed.
Moisture Control Mix
For gardeners who have trouble maintaining consistent watering schedules, a moisture control mix can be a lifesaver.
This mix often includes water-absorbing crystals or other materials that help retain moisture and release it slowly over time. This helps keep the soil evenly moist, reducing the risk of overwatering or underwatering your plants.
Potting Mix Ingredients
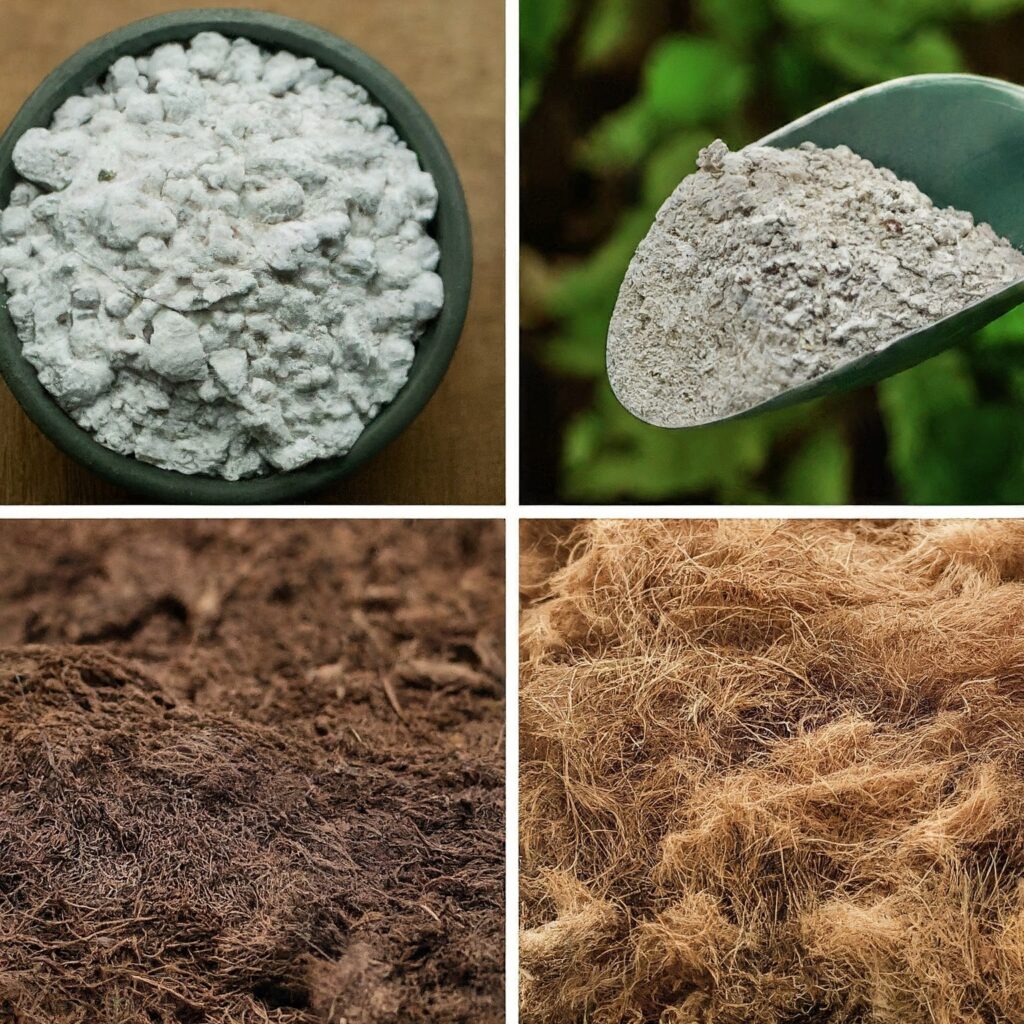

A good potting mix contains several key ingredients, each playing a vital role in creating the perfect environment for your plants.
Here are some common components:
Peat Moss
Peat moss is a staple in many potting mixes. It’s lightweight, retains moisture well, and provides a slightly acidic pH that many plants love.
However, it’s important to note that peat moss is a non-renewable resource, and its harvesting has environmental impacts. Some gardeners prefer to use coconut coir as a more sustainable alternative.
Perlite
Perlite is a volcanic glass that’s heated until it expands, creating a lightweight, porous material. It helps with drainage and aeration, preventing your mix from becoming compacted.
Perlite is especially useful in a succulent mix or any situation where you need to ensure excellent drainage.
Vermiculite
Similar to perlite, vermiculite is a mineral that expands when heated. It also helps with aeration and moisture retention, making it a valuable addition to potting mix.
Vermiculite is often used in seed-starting mixes because it holds moisture well, providing a consistent environment for germinating seeds.
Coconut Coir
Derived from the fibrous hearts of coconut husks, coconut coir is a sustainable and natural material. It is more sustainable alternative to peat moss and has excellent water retention properties.
Coconut coir also has a neutral pH, making it suitable for a wide range of plants. It’s increasingly popular in organic and environmentally conscious gardening.
Composted Bark
Composted bark adds organic matter to the mix, improving its structure and providing nutrients as it breaks down. It also helps with aeration and can contribute to the overall health of the soil.
Composted bark is often found in general potting mixes and can help support healthy root growth.
How to Make Potting Mix at Home – The DIY Way
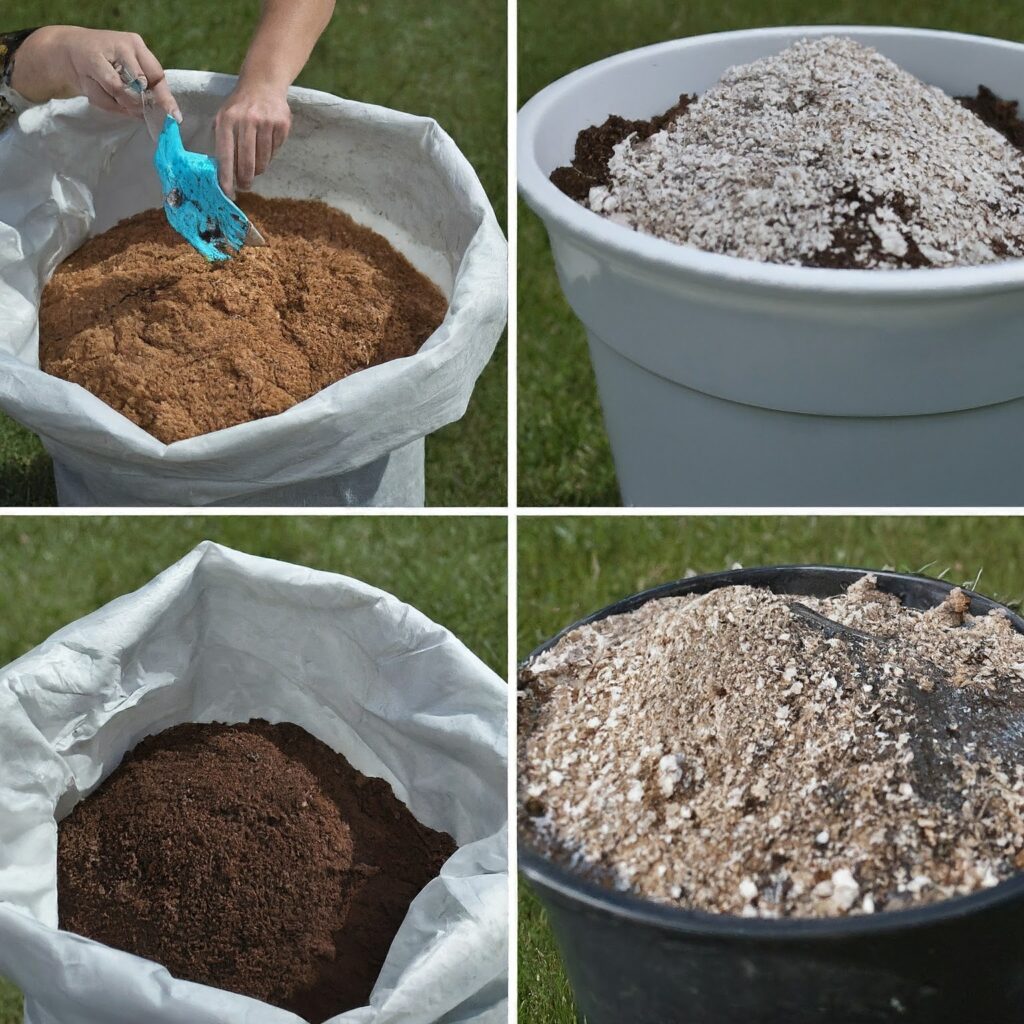

If you’re feeling adventurous, you can make your own potting mix at home.
Here’s how.
Ingredients
- 1 part peat moss or coconut coir
- 1 part perlite or vermiculite
- 1 part composted bark or compost
Instructions
- Measure and Mix: Measure out equal parts of each ingredient.
- Combine Thoroughly: Mix them together in a large container until well blended.
- Store Properly: Store your homemade potting mix in a sealed container to keep it fresh.
Feel free to adjust the recipe based on the specific needs of your plants.
For example, you may want to add more perlite for better drainage in a succulent potting mix. You can also experiment with different ingredients to find the perfect blend for your gardening style.
Here’s a video showing how to make your own potting mix:
Conclusion
Understanding potting mix is essential for any gardener, especially if you’re just starting out. The right mix can provide your plants with the perfect environment to thrive.
Whether you opt for a commercial blend or decide to make your own, remember that the key to successful gardening lies in the quality of your potting mix.
Potting Mix FAQ
Is potting mix just for pots?
While potting mix is made for use in containers, you can also use it in raised beds or as a soil amendment in your garden. Its light and airy texture can improve drainage and aeration in heavy soils, making it a versatile addition to your gardening toolkit.
Is fertilizer and potting mix the same?
No, fertilizer and potting mix are not the same.
Potting mix is a growing medium that provides physical support and some nutrients, while fertilizer is an additive that supplies specific nutrients to plants.
Think of potting mix as the foundation and fertilizer as the ongoing support your plants require.
What’s the difference between potting mix and compost?
Potting mix is a blend of multiple ingredients made for container gardening. It gives a balanced atmosphere for plant root development.
Compost, on the other hand, is decomposed organic matter that enriches the soil with nutrients. While compost can be an ingredient in potting mix, they are not interchangeable.
Potting mix provides the structure and drainage needed for container plants, while compost primarily improves soil fertility.
Does potting mix go bad?
Yes, potting mix can go bad over time. If it becomes compacted, loses its texture, or develops a sour smell, it’s best to replace it.
Old potting mix can also harbor pests and diseases. It’s a good idea to store potting mix in a cool, dry place and to use it within a year for best results.
Can you reuse the potting mix?
You can reuse potting mix if it’s still in good condition. Remove any old roots and debris, and refresh it with new ingredients like compost or fertilizer.
However, if the mix shows signs of pests or disease, it’s better to discard it and start fresh.
Reusing potting mix can save you money and resources, but it’s important to ensure it’s still providing a healthy environment for your plants.
Is it a good idea to add fertilizer to the potting mix?
Yes, adding fertilizer to potting mix can be beneficial. Most commercial mixes contain some nutrients, but they can be depleted over time.
Regularly adding fertilizer ensures that your plants continue to receive the necessary nutrients for healthy growth. Choose a balanced fertilizer and follow the instructions to avoid over-fertilizing, which can harm your plants.