Welcome, aspiring gardeners, to our comprehensive guide on tomato plant staking, caging, and trellising! Today, we’re going to dive deep into the art and science of supporting your tomato plants.
Whether you’re a seasoned gardener looking to refine your techniques or a newcomer eager to learn the ropes, you’ve come to the right place.
Jump to section.
- Types of Plants That Need Support
- What is Staking in Agriculture
- What is Caging in Agriculture
- What is Trellising in Agriculture
- Tomato Plant Staking
- Everything You Want to Know About Good Tomato Cages
- Conclusion
- Tomato Support FAQs
- 1. What to do when the tomato plant grows taller than the stake?
- 2. What should I use to tie the tomato plant to the stake?
- 3. Will the tomato cage overturn when the plant becomes taller?
- 4. How long should tomato stakes be?
- 5. Do all tomatoes need staking?
- 6. What is the best way to stake determinate tomatoes?
- 7. How do you stake tomatoes in pots?
- 8. What is double staking tomatoes?
Types of Plants That Need Support
First things first, what types of plants need a support system? While tomatoes are the stars of the show in our discussion today, they’re not the only ones that require support. Other plants that often need a helping hand include:
- Vegetables: Think cucumbers, peppers, and beans—these vining vegetables can sprawl in all directions without proper support.
- Flowering Perennials: Delicate flowers like aster and dahlias may require support to prevent them from drooping or bending under their weight.
- Saplings: Young trees and shrubs can benefit from staking to encourage straight and healthy growth.
- Top-Heavy Houseplants: Large, leafy houseplants such as peace lilies and rubber trees may topple over without adequate support, especially as they grow taller.
Now that we’ve identified the candidates for support, let’s explore the different support systems used in agriculture.
What is Staking in Agriculture
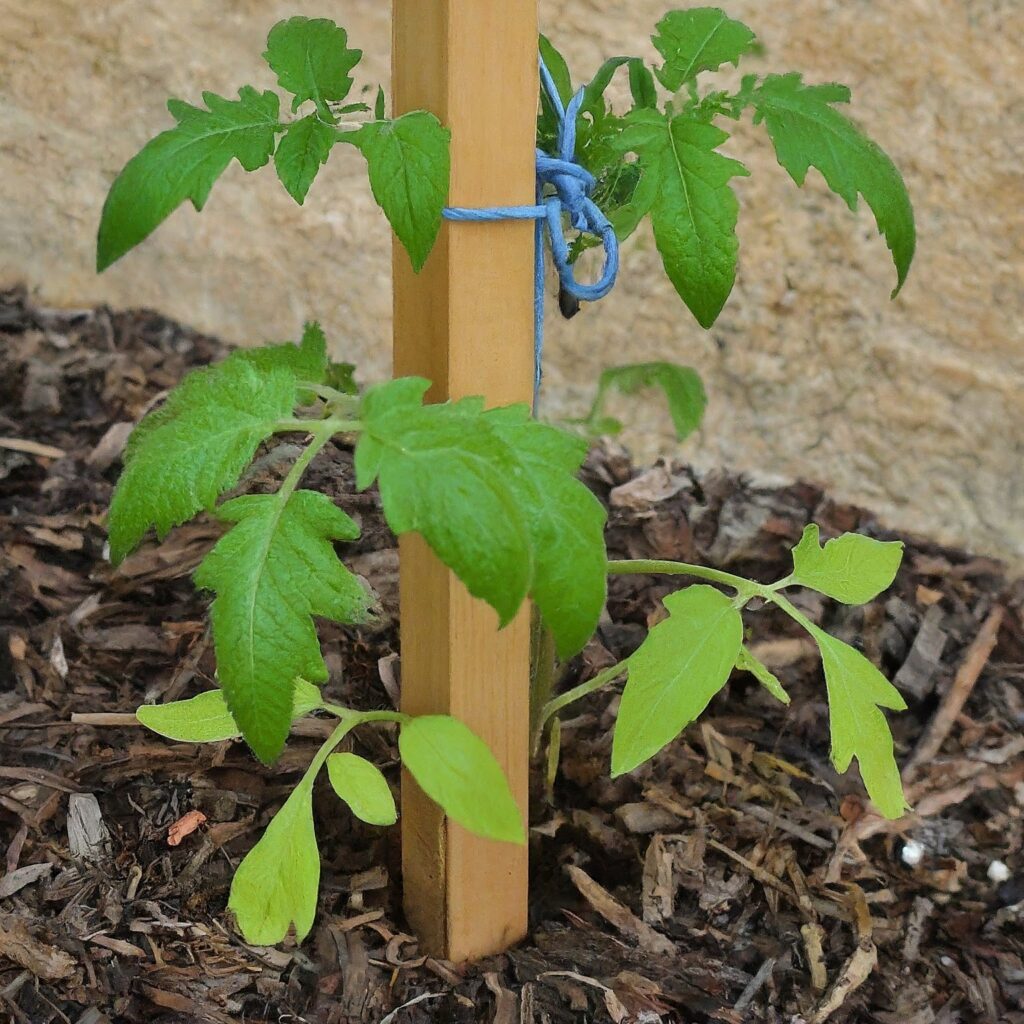

Staking is a common practice that many agriculturists and gardeners use to support plants. They do so by securing them to a sturdy stake. This method is particularly popular for tall or top-heavy plants like tomatoes, ensuring they remain upright and stable throughout their growth cycle.
Now, picture this: You’ve got a young tomato plant, small and delicate at first, but it’s got big plans to grow tall as it matures. Without support, though, its leaves and fruits might weigh it down, causing it to lean or even collapse. Not good for your plant’s health or the amount of tomatoes you’ll get!
So, what do you do? You stake it! It’s like giving your tomato plant a strong backbone to lean on as it grows. You’re preventing potential problems and ensuring it has the stability it needs to thrive.
Think about it this way: Just like how a trellis helps climbing vines reach new heights or a crutch supports someone with a broken leg, staking your tomato plant keeps it strong and healthy.
To sum it up, when you’re gardening, staking plants is crucial, especially for tall or top-heavy ones like tomatoes. It’s all about keeping them upright, stable, and thriving throughout their growth journey.
Importance of Staking
Staking is done for several essential purposes in gardening.
- Firstly, it prevents plants from sprawling on the ground, reducing the risk of disease and pest infestations.
- Secondly, it saves the day by preventing the plants from bowing or snapping under the weight.
- Thirdly, it promotes better air circulation around the plant, which is essential for preventing fungal infections.
- Finally, staking helps maximize sunlight exposure, allowing plants to photosynthesize more efficiently and produce healthier yields.
Types of Staking
When it comes to staking, there are several methods you can use. Each of them has its pros and cons.
Some of the common staking techniques include:
1. Single Staking Method
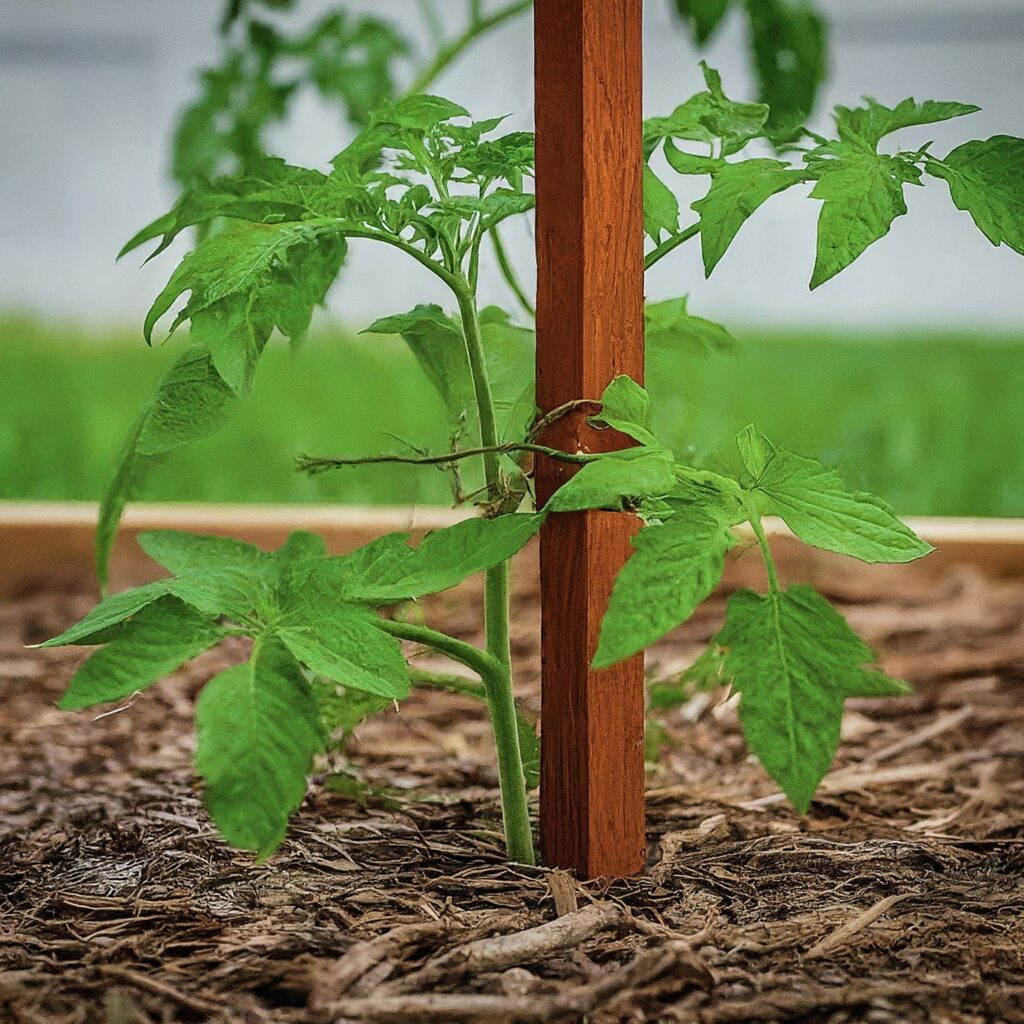

In this approach, a single stake is driven into the ground next to the plant, and the main stem is gently tied to the stake as it grows.
2. Double Staking Method
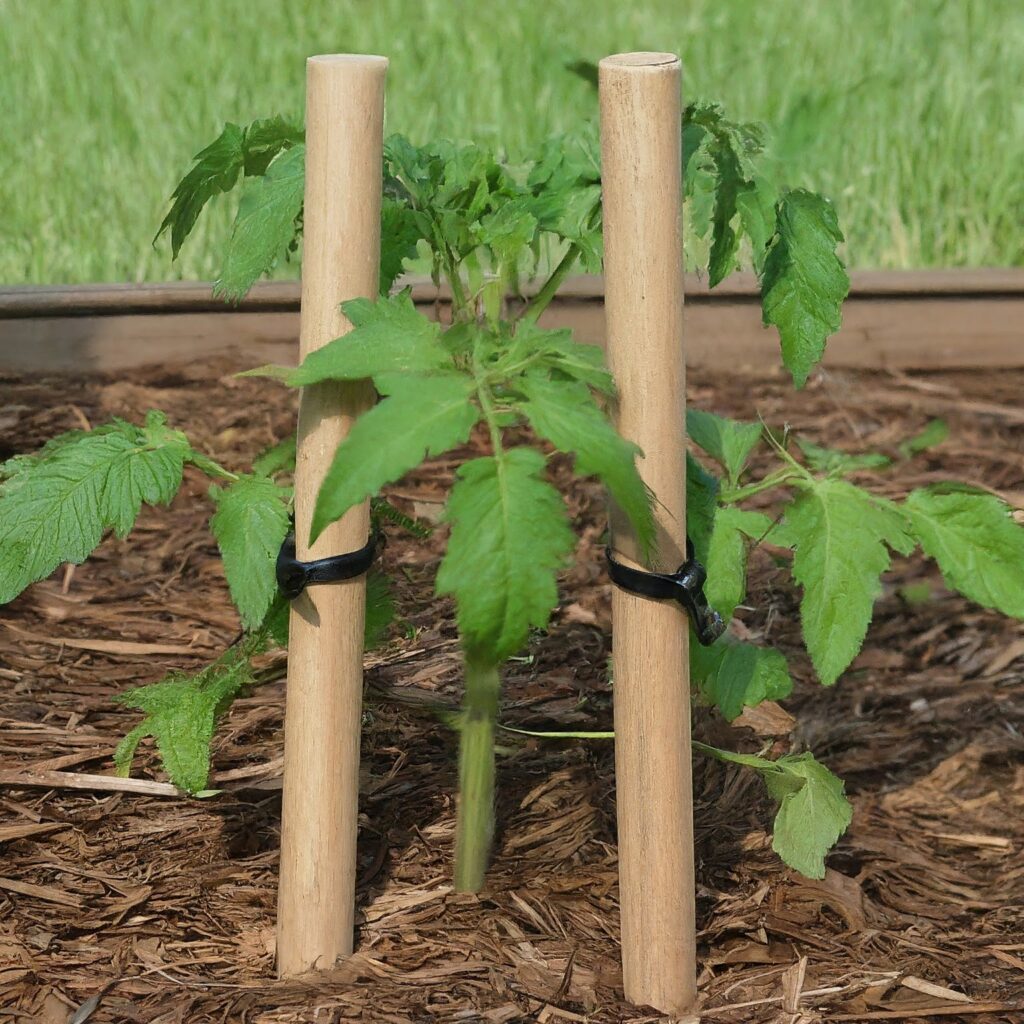

Similar to the single staking method, but with two stakes placed on either side of the plant for added support.
3. Cage and Stake Method
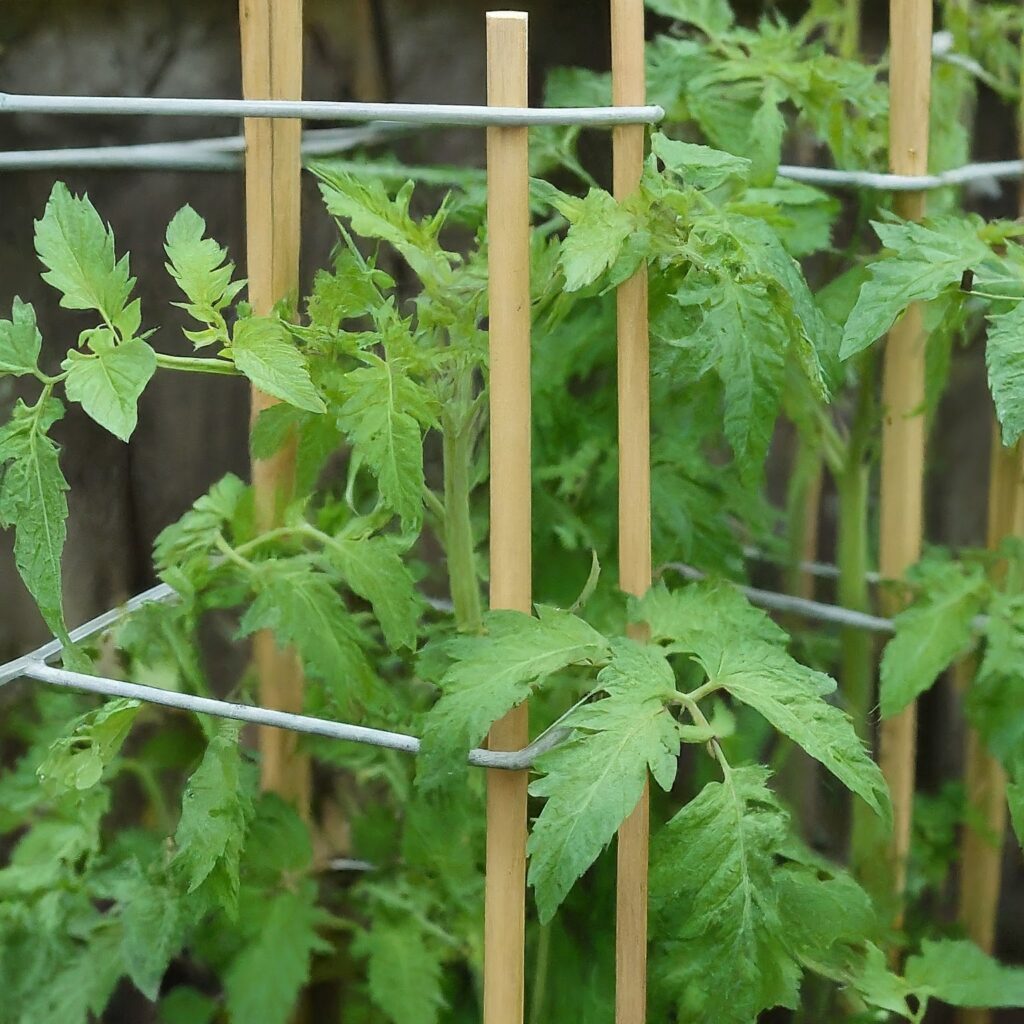

This hybrid approach combines staking and caging, providing both vertical and lateral support for the plant.
Now that we’ve covered staking, let’s turn our attention to another popular support method: caging.
What is Caging in Agriculture
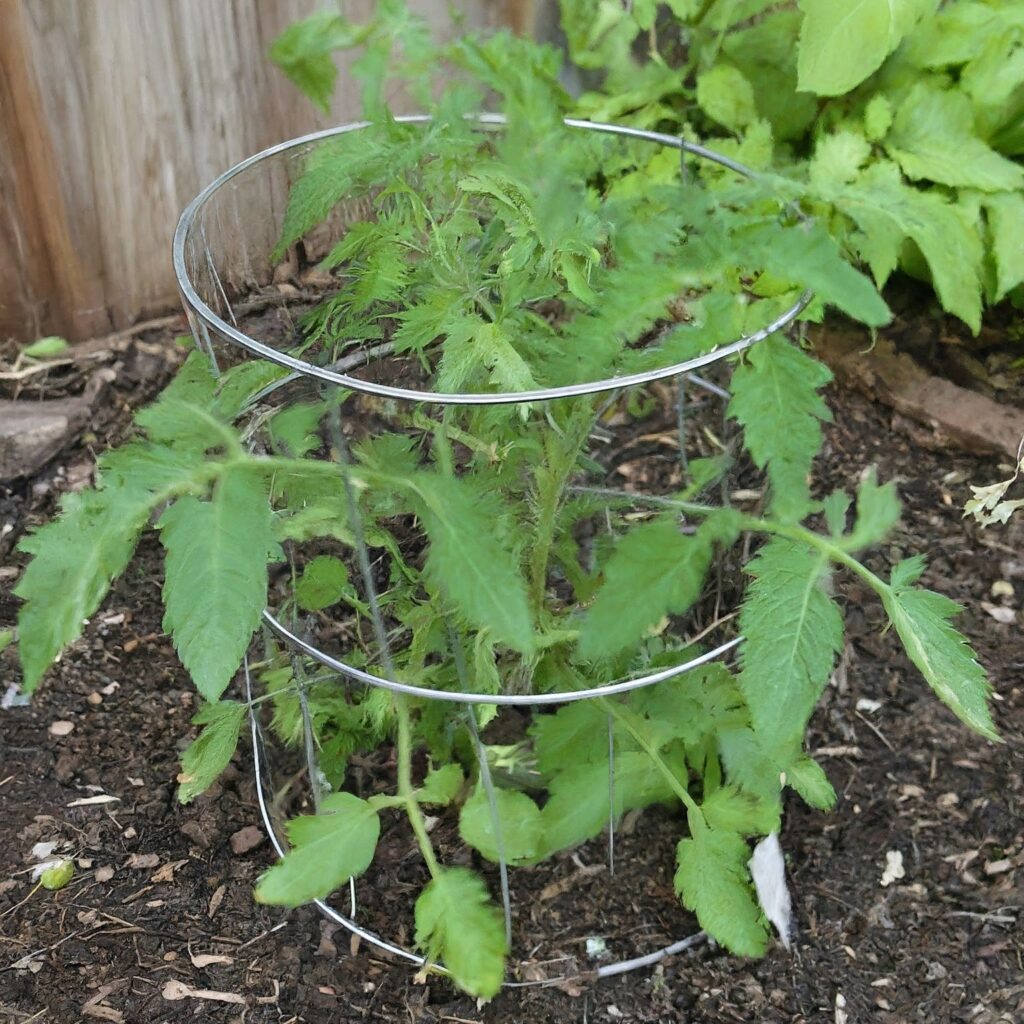

Caging involves placing a wire or wooden cage around a plant to provide support and structure as it grows. This method is commonly used for plants like tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants, which tend to sprawl outward as they mature.
Importance of Caging
Caging offers several benefits for gardeners.
First, it provides 360-degree support, ensuring that plants remain upright and contained as they grow. Second, it allows for easy access to the plant for pruning, harvesting, and pest management.
Finally, caging helps to protect delicate fruits from touching the ground, reducing the risk of rot and disease.
Types of Caging
When it comes to caging, there are various options to choose from, ranging from homemade DIY cages to commercially available products.
Some popular types of tomato cages include:
1. Wire Tomato Cages
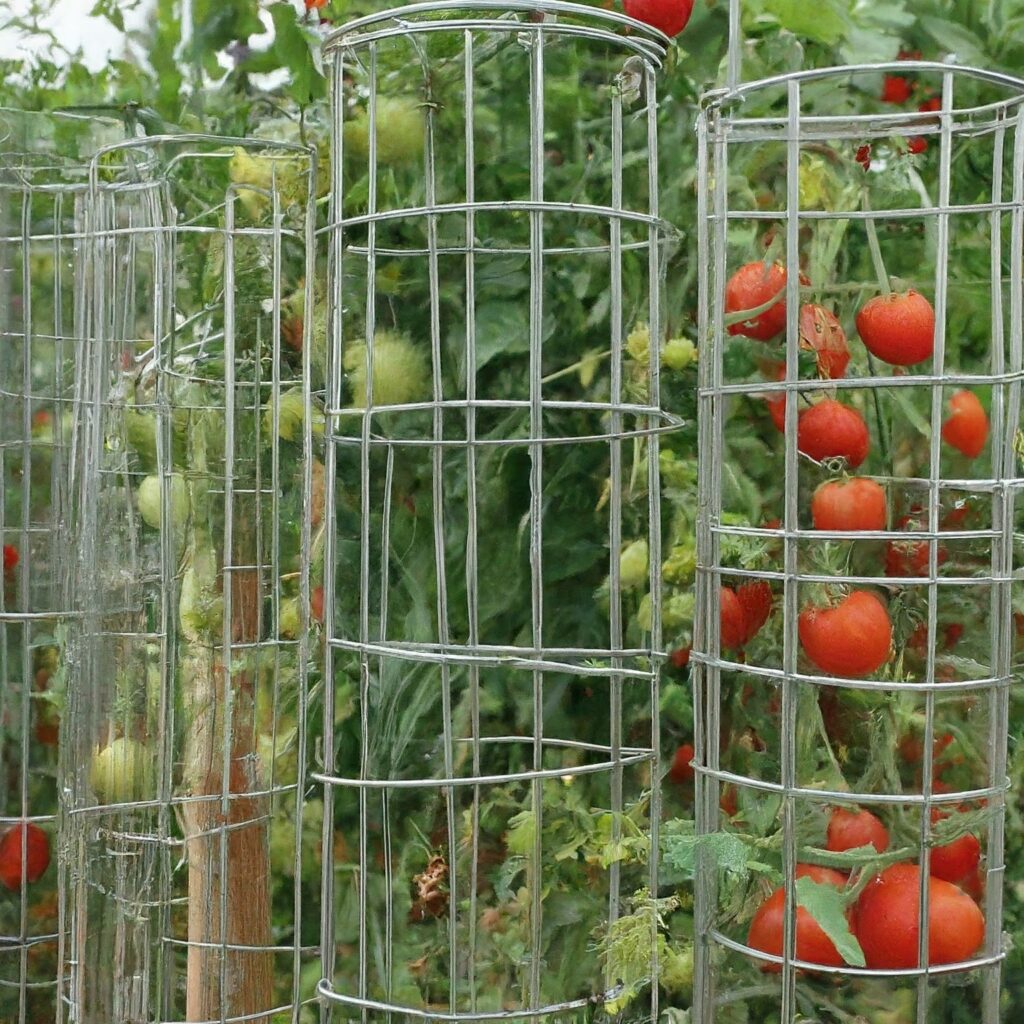

These sturdy cages are made from galvanized wire and come in a range of sizes to accommodate different plant heights.
2. Wooden Tomato Cages
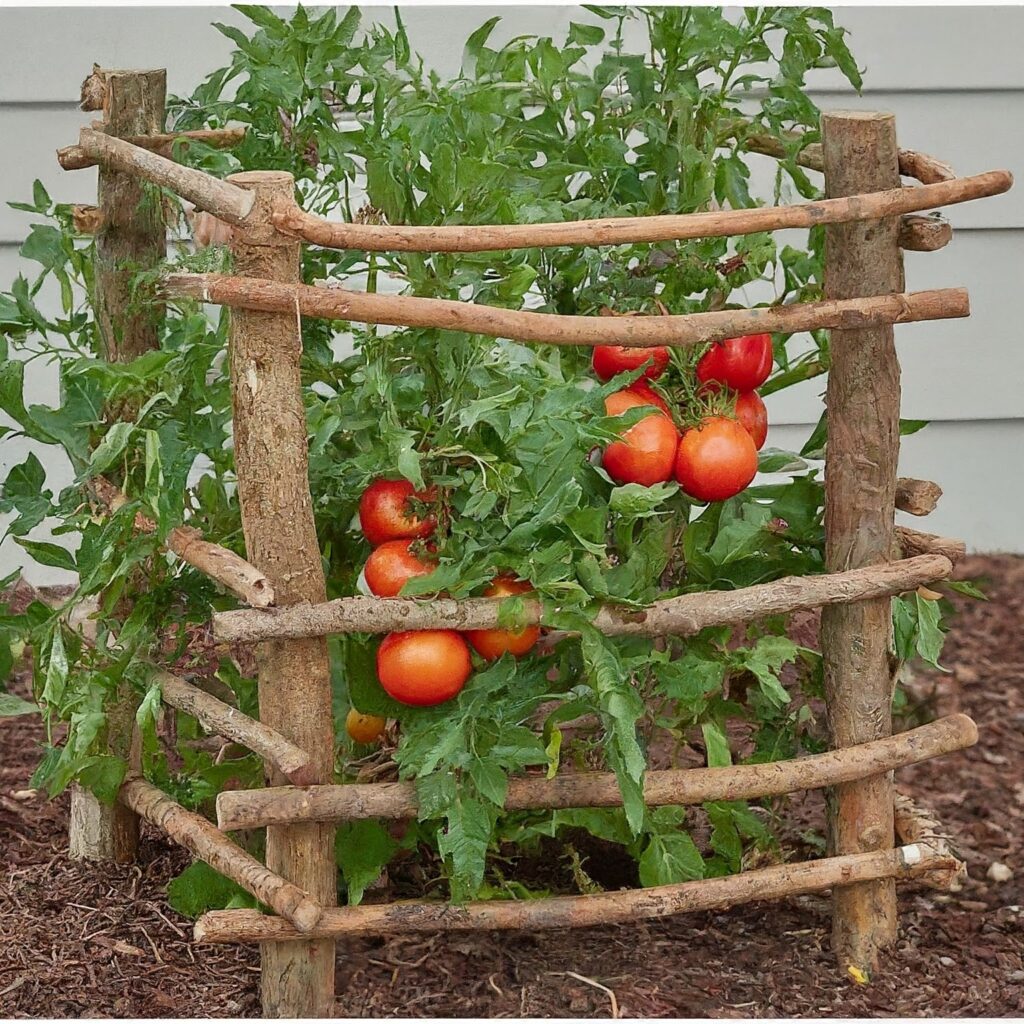

Made from sturdy wooden stakes or branches, these homemade cages offer a rustic and eco-friendly alternative to traditional wire cages.
3. DIY Tomato Cages
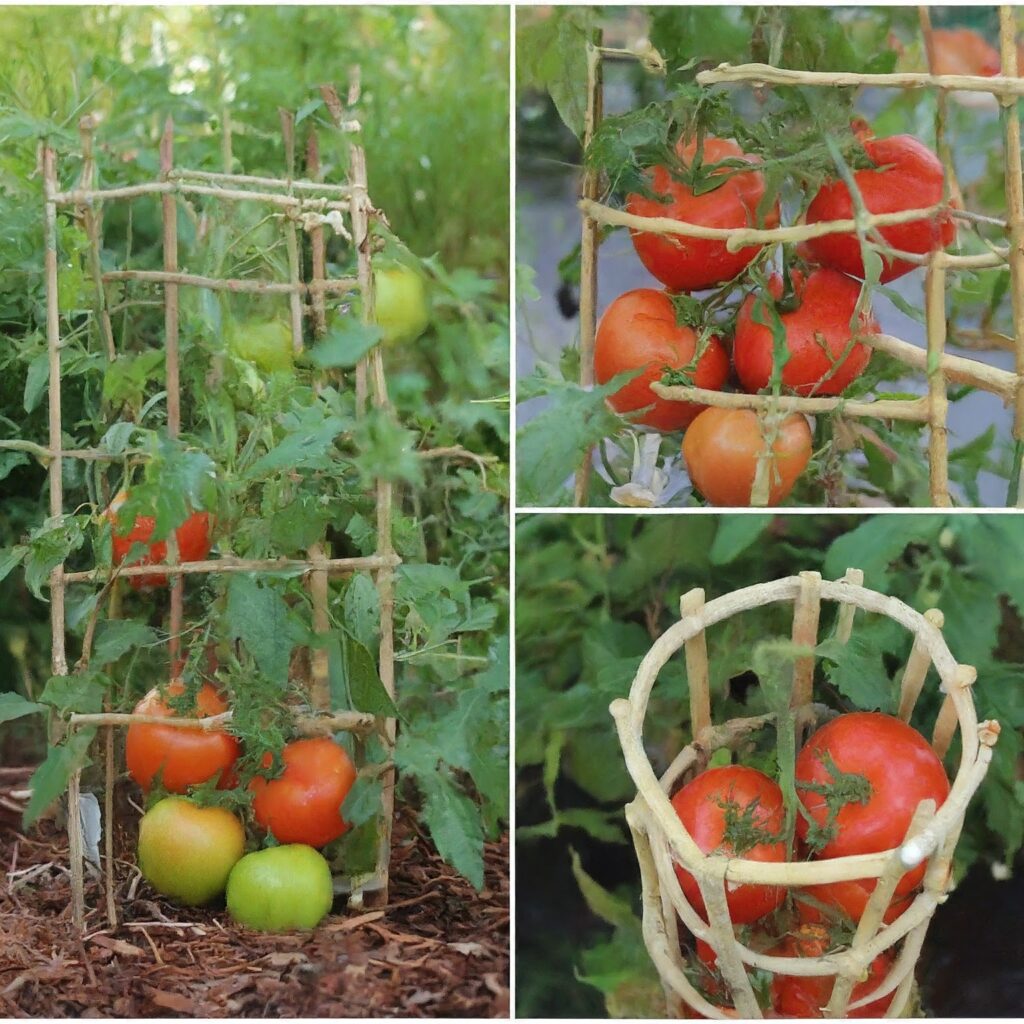

Get creative and make your own tomato cages using materials like bamboo, PVC pipes, or even recycled materials like old wire fencing.
Now that we’ve explored staking and caging, let’s move on to another support method: trellising.
What is Trellising in Agriculture
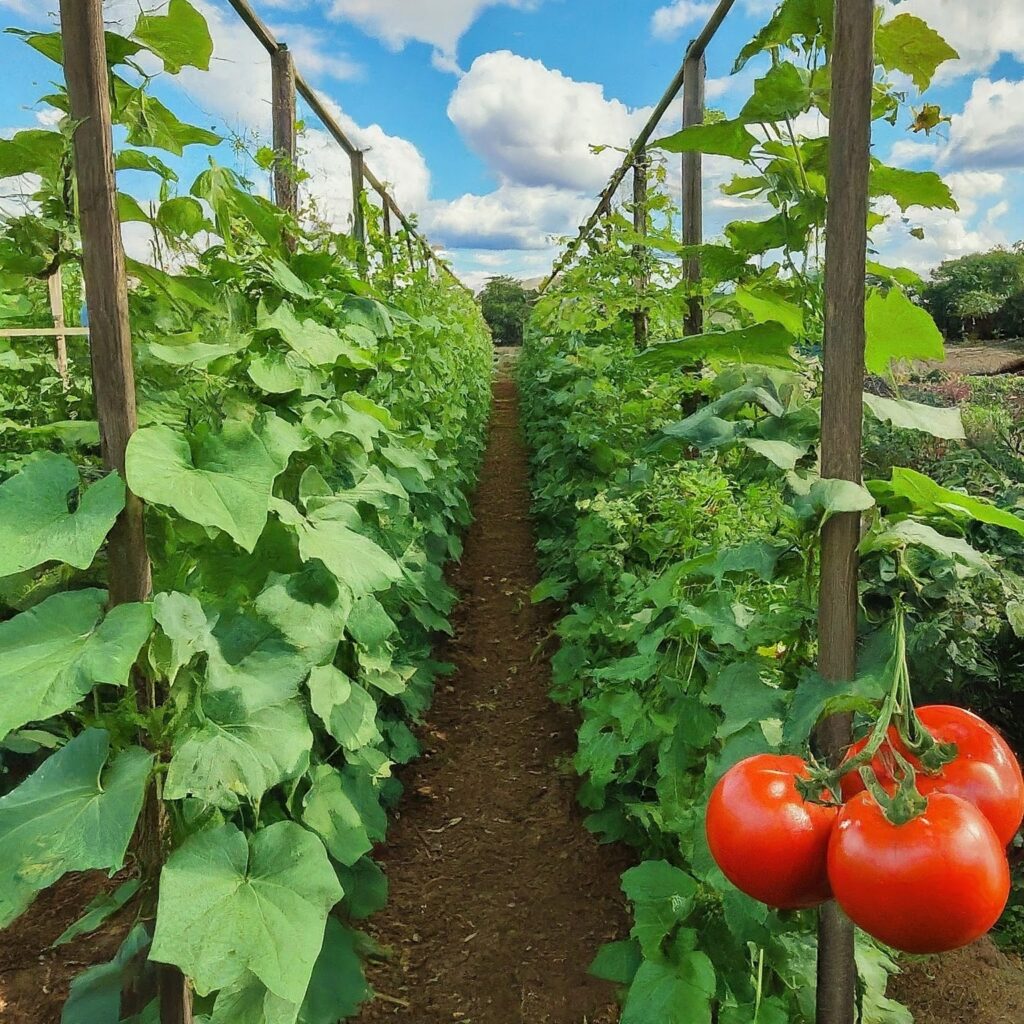

Trellising involves training plants to grow vertically along a structure, such as a trellis or arbor. This method is commonly used for vining plants like cucumbers, peas, and grapes, but can also be adapted for tomatoes with proper support.
Importance of Trellising
Trellising offers several advantages for gardeners. It maximizes space in the garden by encouraging plants to grow upward rather than outward.
Secondly, it promotes better air circulation around the plant, reducing the risk of fungal diseases. Trellising also makes it easier to harvest fruits and manage pests, as plants are more accessible and better organized.
Types of Trellising
When it comes to trellising, there are numerous options available, depending on your garden layout and personal preferences.
Some common types of trellising include:
1. A-Frame Trellis
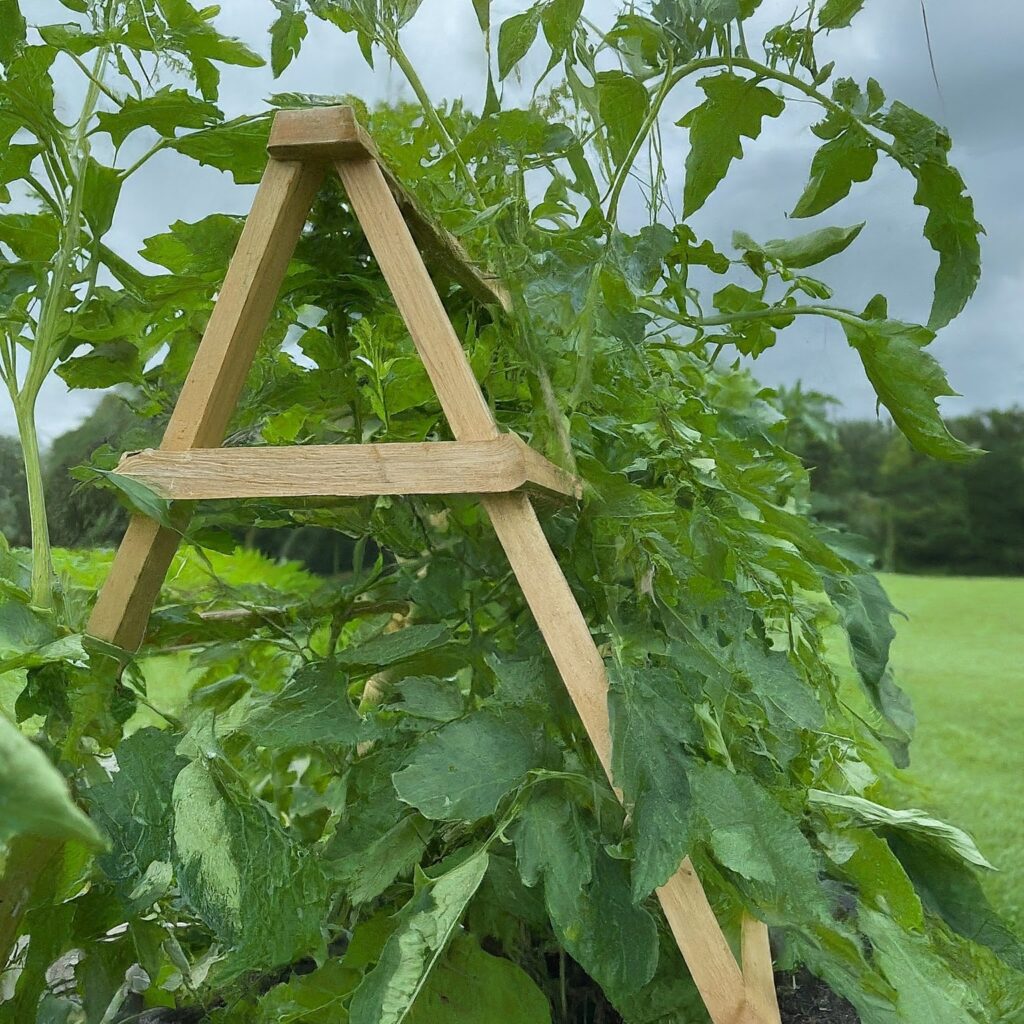

This simple yet effective trellis consists of two vertical posts connected by a horizontal crossbar, forming an A-shape. Plants are trained to grow up the crossbar, providing support as they climb.
2. Teepee Trellis
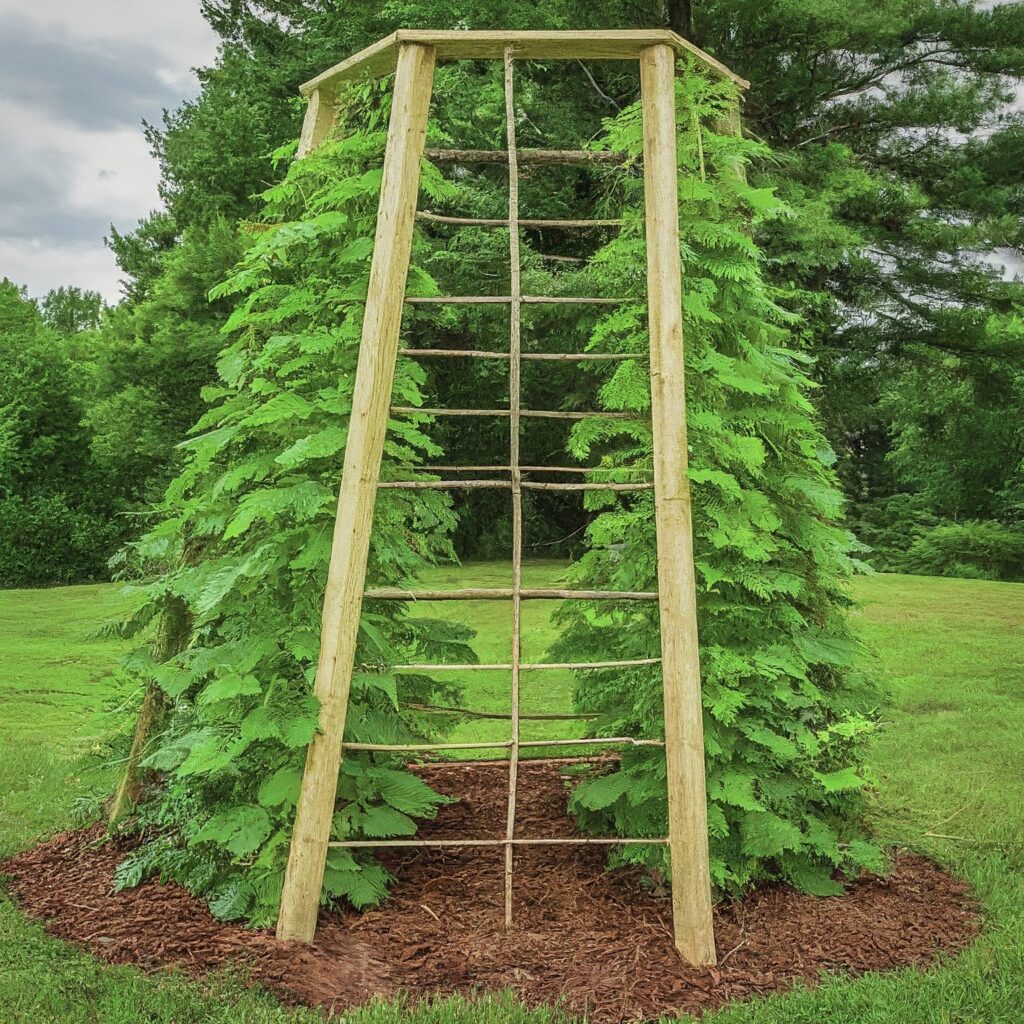

Similar to the A-frame trellis, but with three or more vertical posts arranged in a cone shape. Plants are trained to grow up the sides of the teepee, creating a beautiful and functional garden feature.
3. Wall Trellis
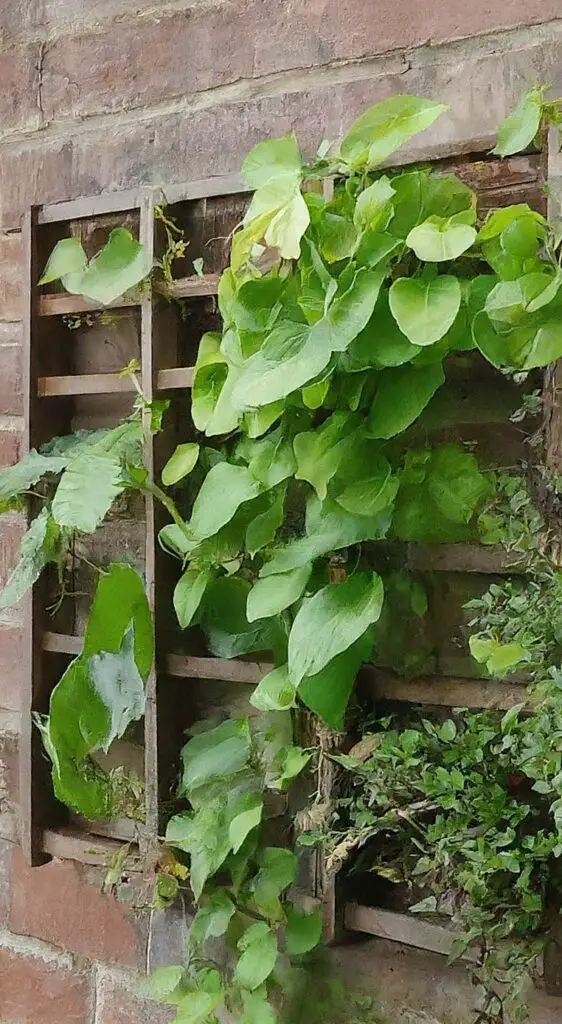

Perfect for small gardens or urban spaces, wall trellises are attached to a vertical surface, such as a fence or wall. Plants are trained to grow vertically along the trellis, saving valuable ground space.
Now that we’ve covered the basics of staking, caging, and trellising, let’s focus specifically on tomato plant support and explore the various methods available.
Tomato Plant Staking
Tomatoes are notorious for their sprawling growth habit, making them prime candidates for staking. Fortunately, there are several methods you can use to support your tomato plants and ensure a bountiful harvest.
Tomato Staking Methods
When it comes to staking tomatoes, there are several tried-and-true methods to choose from. We’ve generally explained them above but let’s go over how to use them specifically for tomatoes.
- Single Stake Method: Drive a sturdy wooden or metal stake into the ground next to the tomato plant, being careful not to damage the roots. As the plant grows, gently tie the main stem to the stake using soft twine or fabric strips. Be sure to leave some slack in the ties to accommodate the plant’s growth.
- Double Stake Method: Similar to the single stake method, but with two stakes placed on either side of the plant for added support. This method is particularly useful for large or top-heavy tomato varieties.
- Cage and Stake Method: Combine the benefits of staking and caging by placing a wire cage around the tomato plant and securing it to a sturdy stake. This hybrid approach provides both vertical and lateral support, ensuring that your tomato plants remain upright and stable as they grow.
Now that you know the basics of tomato plant staking, let’s explore another essential aspect of tomato support: choosing the right tomato cages.
Everything You Want to Know About Good Tomato Cages
When it comes to supporting your tomato plants, choosing the right cages is essential. A good tomato cage should be sturdy, durable, and large enough to accommodate the plant’s growth.
Here are some key factors to consider when selecting tomato cages:
- Material: Tomato cages are typically made from either galvanized wire or wood. Galvanized wire cages are durable and long-lasting, while wooden cages offer a more natural and rustic aesthetic.
- Size: Choose a tomato cage that is tall and wide enough to support your tomato plants as they grow. Ideally, the cage should be at least 4-5 feet tall and 18-24 inches in diameter to accommodate larger tomato varieties.
- Stability: Look for cages with sturdy legs or stakes that can be securely anchored into the ground. Avoid lightweight cages that may topple over in strong winds or heavy rain.
- Ease of Use: Go for cages that are easy to install and maintain, with simple assembly and disassembly for storage during the off-season.
Staking Tomato Plants With Bamboo
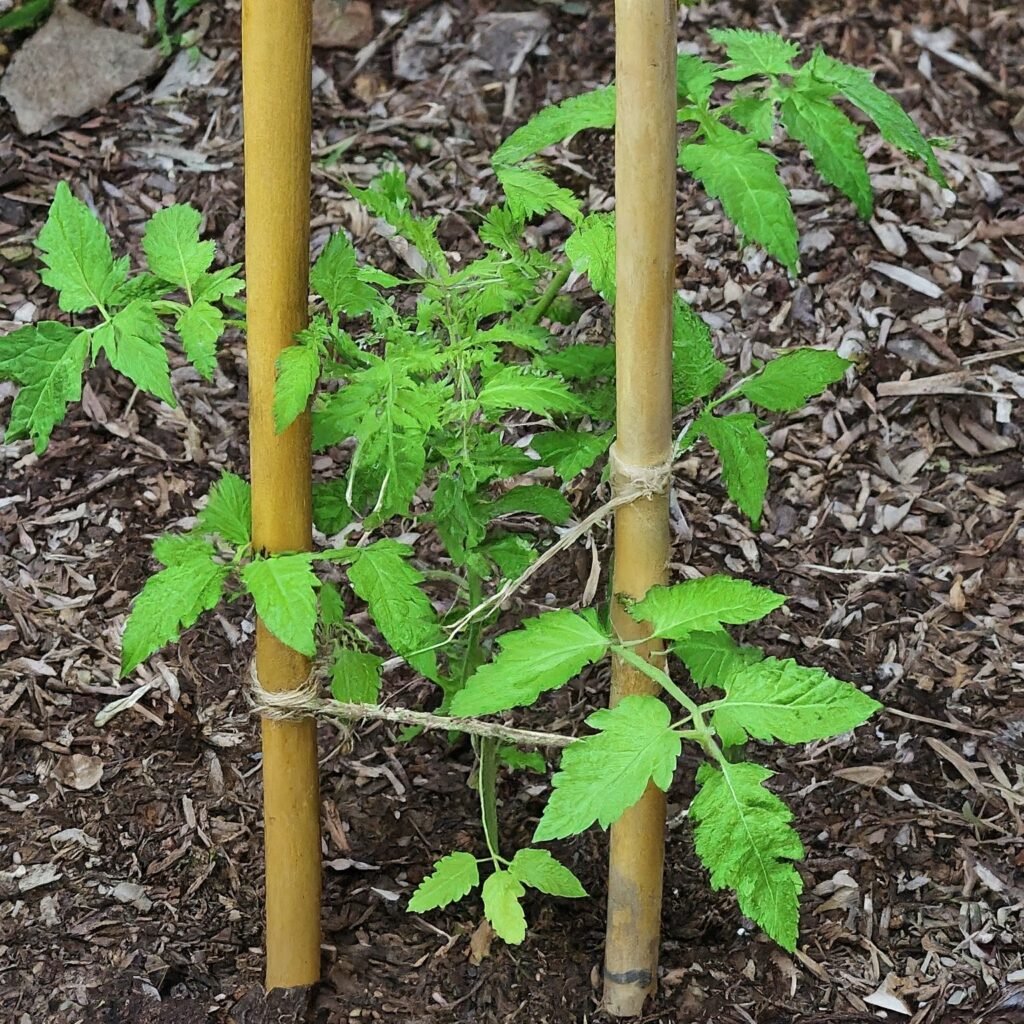

If you’re looking for a budget-friendly and eco-friendly alternative to traditional tomato cages, consider staking your tomato plants with bamboo. Bamboo stakes are readily available at garden centers and are easy to work with, making them an excellent choice for DIY tomato support.
To stake your tomato plants with bamboo, follow these simple steps:
- Choose sturdy bamboo stakes that are at least 6-8 feet tall and 1-2 inches in diameter.
- Drive the bamboo stakes into the ground next to the tomato plants, spacing them evenly around the perimeter of the plant.
- Gently tie the main stem of the tomato plant to the bamboo stakes using soft twine or fabric strips, leaving some slack in the ties to accommodate the plant’s growth.
- As the plant grows, continue to tie it to the bamboo stakes at regular intervals, ensuring that it remains upright and supported.
Conclusion
Congratulations, you’ve reached the end of our comprehensive guide to tomato plant staking, caging, and trellising! You’re now well-equipped to support your tomato plants and enjoy a bountiful harvest all season long.
Whether you choose to stake, cage, or trellis your tomatoes, remember to prioritize sturdy support structures, adequate spacing, and regular maintenance for optimal results. Happy gardening!
Tomato Support FAQs
1. What to do when the tomato plant grows taller than the stake?
If your tomato plant outgrows its stake, you can either replace the stake with a taller one or use additional stakes to provide extra support.
2. What should I use to tie the tomato plant to the stake?
Soft twine or fabric strips are ideal for tying tomato plants to stakes, as they won’t damage the plant’s delicate stems.
3. Will the tomato cage overturn when the plant becomes taller?
To prevent the tomato cage from toppling over, make sure it is securely anchored into the ground and use additional support stakes if necessary.
4. How long should tomato stakes be?
Tomato stakes should be at least 6-8 feet tall to accommodate the plant’s growth throughout the season.
5. Do all tomatoes need staking?
While not all tomatoes require staking, indeterminate varieties, in particular, benefit from the added support to prevent sprawling and improve airflow.
6. What is the best way to stake determinate tomatoes?
For determinate tomatoes, a single stake or cage can provide adequate support, depending on the size and growth habits of the plant.
7. How do you stake tomatoes in pots?
When staking tomatoes in pots, use a sturdy stake or cage that can be anchored into the soil to provide support as the plant grows.
8. What is double staking tomatoes?
Double staking involves placing two stakes on either side of the tomato plant for added support, particularly for large or top-heavy varieties.